The Challenge
For all terminals at Heathrow Airport, the airside operational management team asked AiQ to estimate the economic and sustainable impact of replacing current ramp equipment to electric Ground Support Equipment (GSE).
This sustainability study is part of Heathrow’s commitment to operating a net zero-carbon airport infrastructure by mid-2030s, supporting the overall UK aviation industry allegiance to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. Heathrow Airport is participating in the international Airport Carbon Accreditation scheme and has achieved level 3 Optimisation requiring third party engagement in carbon footprint reduction.
Our challenge was to support a business case by estimating the environmental carbon savings of converting to electric in addition to determining the power and number of EV electric charge point requirements at all terminals for efficient operations.
The Solution
Working closely with the airside operational team, AiQ observed, assessed, and modelled the current ramp equipment and its activity including pushback tugs, ramp team vans, steps, ULD loaders and conveyors across all terminals.
A vehicle register was provided by HAL containing the Euro classification for each vehicle. This was used to determine the average CO₂ (Carbon Dioxide) emissions for each vehicle type. This varies by the handler as they have different age profiles for their GSE fleets. A range of emissions for aircraft tugs, conveyors, motorised passenger steps and ULD lifters calculated using the European emission standards for heavy-duty diesel engines and EU non-road mobile machinery standards.
For the purposes of this study, the equipment journey assumption started from its parking position, attending the aircraft, and then returning to the same parking position. Parking observations were also made by AiQ.
To estimate the power and number of EV charging points, our model assumptions were based on a range of datasheets and technical specifications from external sources determining the battery capacities, charging times, battery drain, rates of power for all the required electric vehicles.
Our simulation engineers used our bespoke modelling and simulation software, TransvisionAiR® to estimate the below:
- The current CO₂ emissions
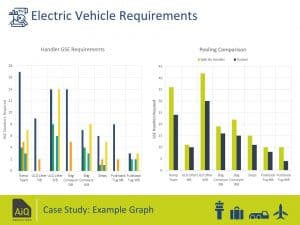
- Electric vehicles requirements – Handlers v’s pooling comparison
- Elective vehicles charging spaces (conventional charging & rapid charging)
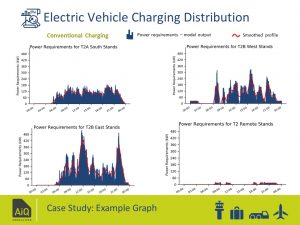
- Electric charging distribution in stand group locations (conventional charging & rapid charging)
- Electric Vehicle conversation rate – % of electric vehicles by GSE type, Quarterly emissions, Quarterly power
The outputs were produced in a range of visual graphs, timeline graphs, comparative tables, and terminal maps to enable smart decision for efficient operations and decarbonising the airport’s infrastructure.
The Benefits
Our client was very pleased with our results providing clear information to help Heathrow build a more efficient, sustainable and net zero-carbon airport. Recommendations were also presented with the results to reduce mileage and ideas to help implement electric vehicles in the future such as allocation systems.
- CO₂ emissions reduction
- Contribution to Heathrow’s level 3 optimisation Airport Carbon Accreditation Scheme
- Efficient resource utilisation
- Future-proofing airport for sustainable growth
- Efficient stakeholder management
- Increasing airport sustainability
- Clear comparisons & evaluation of options for future decision making
- Use of data to provide effective electric vehicle planning
- Integrated technology